Facebook Ads Tutorial
A Beginner’s Guide to Facebook/Meta Ads
If you remember nothing else in this Facebook Ad Tutorial, remember this…
- Facebook/Meta Ads is a direct marketing platform.
- Users on Facebook/Meta are not comparing or shopping around. In most cases, they are being distracted from their activity with an eye-catching ad.
- Factors that help you increase your results are quality landing page experience, logical post-click action, audience, and placements.
- Understand your KPI targets and build on them. Track your performance over time and optimize until you reach your targets.
- Your pixel/cAPI must be placed correctly on your site if you plan on using external landing pages.
Using Facebook/Meta Ads to generate traffic
There are many ways to use Facebook/Meta ads to generate traffic. In general they can be broken down into the following:
- Ad to landing page
- Ad to Messenger
- Ad to offer
- Ad to form (lower quality leads)
The main use case for nearly every business that I’ve worked with is Facebook/Meta Ad to landing page. Messenger and offer campaigns are effective, but can be considered more advanced techniques and strategies for once you have your basic funnel mapped out.
How Facebook/Meta ads work
- Advertisers publish an ad on Facebook/Meta’s self-serve platform and compete against each other in a marketplace based on their audience targeting.
- When a user matches the advertiser’s targeting criteria, Facebook/Meta delivers an ad at the appropriate moment, called an impression.
- If the user responds to the advertisement by liking, sharing, commenting, or playing a video, Facebook/Meta counts that as an engagement.
- If the user responds to the ad’s call to action—often a click, message or a comment— then the user takes a step down the funnel.
- From that point in the funnel, it is up to the advertiser to optimize the experience and manage the conversion elements. Facebook/Meta’s job is to put the ad in front of the user with the highest probability of accomplishing the campaign goal.
- Factors that will help your campaign perform well include creative, funnel, campaign type, audience targeting, and placement.
Remember that the goal of Facebook/Meta ads is to provide the most relevant and engaging ad and offer to the preferred audience. Therefore, a good user experience and clear message is essential to campaign success.
Relevant key Facebook/Meta Ads terms defined
Key Facebook/Meta Terms
- Account – Each business should have an individual Facebook/Meta Ad account.Campaign – Each campaign refers to an overarching goal that the advertiser wants to achieve.
- Ad set – Each ad set is a particular target for the overarching campaign goal. This is where you set the targeting criteria for your ad.
- Ad – The actual asset that the user sees is called an ad. The ad could be an image, video, or group of images. The ad can be static or dynamic.
- Static ad – An ad that doesn’t rotate with another high performance ad. This is controlled at the ad set level.
- Dynamic ad – An ad that can rotate amongst other ads within the Facebook/Meta ecosystem. This is a tool used for quickly split-testing many ad variations and is controlled at the ad set level.
- Page post – A post made by the page admin. This can be used as an ad.
- Page admin – A user who represents the business and is responsible for the page content.
- Dynamic Product Ads (DPA) – This is a special type of eCommerce Facebook ad type. This type of ad is generated by a product feed uploaded to Facebook and ads are auto-created based on the content within that feed. DPAs are especially useful in an eCommerce retargeting strategy.
- Page – The centralized location of all the business’s assets. This can include a website, reviews, followers/likes, phone number, posts, and comments.
- Custom conversion – A custom, user-defined conversion event that is not one of the standard events included with Facebook/Meta. An example of this is a PreLead—this is when a lead’s information has been captured after landing on a page, but they have not yet been qualified.
- Custom audience – An audience created using Facebook/Meta’s audience tool. Audiences can be built from various sources, including your website traffic, your customer list, your app activity, your offline activity, your Facebook/Meta videos, your Instagram business profile, your lead form, your events, your instant experience, or your Facebook/Meta Page.
- Look-a-like audience (LAL or LLA) – After building a custom audience, you can build a look-a-like with various levels of similarity (1%-10%). A look-a-like should behave like the source audience. The greater the %, the less overlap the audience will have with the source audience.
- Return on ad spend (ROAS) – The multiple of your return compared to your spend. If you have a 4x ROAS, then you spend $1 and get $4 back.
- Breakdowns – Once you’ve identified the correct placement that you want to pursue, you can see it in the breakdown. Breakdowns provides you granular data about your audience so you can see how well your ad performed in certain market segments.
- Campaign budget optimization (CBO) – This is the campaign setting that allows Facebook/Meta to determine the allocated budget per ad set, compared to a static value at the ad set level.
Key factors for Facebook/Meta ad success
- Creative – The actual ad of the campaign. This can be an image, or video.
- Campaign goal – The type of traffic that will be delivered to your creative. There are currently 13 goals to choose from.
- Landing page – The page the user lands on after they click on the ad.
- Funnel – The user experience after they view the landing page.
- Pixel – The data bridge between your website and Facebook/Meta’s platform. This transmits the data that Facebook/Meta needs to optimize campaigns. This is especially important for conversion-oriented campaigns.
- Ad account – Each ad account will perform differently to some degree. 2 Campaigns on 2 different accounts targeting the same criteria will perform differently depending on many factors.
- Audience – The audience that you target with your ads. This can include demographics, interests, and device type.
- Placement – The placement of your ads on Facebook/Meta’s assets.
Best practices for Facebook/Meta Ad success
Creative
As the name suggests, you need to get creative here:
- Research your competition’s ads.
- Test many images/videos, headline, and text combos using the Dynamic Ad Toggle on the ad set level (only available on certain campaign types).
- Images can be from Shutterstock on Facebook/Meta, custom images, or from free websites.
- Use striking, scroll-stopping images and videos. Think outside the box—they don’t necessarily have to relate to the offer.
- Videos can be stock videos or custom-made product videos. Think about social engagement here. What’s likely to go viral will likely perform well with Facebook/Meta Ads.
- Focus your copy on connecting with the target audience.
- Create a singular, focused call to action from the creative that you want your audience to respond to.
- Include the link or call to action inside of your copy.
Campaign goal
- Choose a campaign goal that fits your offer’s objectives. If you want leads, sales, or an acquisition of some sort, choose conversion as your campaign goal.
- Facebook/Meta offers many different campaign types. Each campaign type is effective for its particular goal. Facebook/Meta refers to these as “Campaign Objectives”.
- These objectives are available at the time of writing this:
- Brand awareness
- Reach
- Traffic
- App Installs
- Video Views
- Lead Generation
- Post Engagement
- Page Likes
- Event Responses
- Messages
- Conversions (Now Sales)
- Catalog Sales
- Store Traffic
- When running conversion campaigns, test to see which conversion will bring the best results:
- View content
- Add to cart (eCommerce)
- Initiate checkout (eCommerce)
- Purchase (eCommerce)
- Lead
- Set the campaign budget so that you have enough spend for your selected audience and the number of ad sets within the campaign (i.e., don’t put a $10/day budget on a campaign with 5 ad sets and an audience of 5M). It will take too long to optimize and you won’t get results fast enough for machine learning to engage.
Facebook Bid Strategy
- Highest Volume
- ROAS Goal
- Cost per Results Goal
- Bid Cap
Pro tips: Campaigns can be used as stand-alone or as part of a broader, more advanced campaign goals. For example, you can have two simultaneous campaigns running for a video. One can be a video view campaign to increase social engagement, and the other can be a campaign to increase conversions.
In the beginning, it’s important to first understand the offer that you are running and find a suitable campaign objective for it. Each campaign objective will also be priced differently. In general, video views and post-engagement (pay per engagement) are going to be cheaper compared to a conversions campaign. This is because of how Facebook/Meta optimizes and how its machine learning works.
All ads start in the Learning phase. During this phase, Facebook/Meta’s machine learning, AI-driven algorithm finds the best audience to fit the goal. In theory, and if your ad is engaging, prices should stabilize or decline. If your ad is not engaging and it is costing Facebook/Meta more compared to other ads in the marketplace, the price will gradually increase. This ebb and flow happens naturally during the Learning phase of an ad’s growth.
Generally, after some time in the marketplace, your ad will be matured. Once the ad is matured, expect relatively steady metrics. We know this happens when the ad is more or less stable on a day-to-day basis, until it burns out or needs to be refreshed.
Landing page
- Your landing page should be mobile-responsive.
- A landing page should have a clear next step and singular call to action or purpose.
- Don’t mix up your CTAs on a single page—take the user through a series of steps instead.
- The landing page should contain images, video and textual content to support the benefits of the offer.
- Focus on the benefits to the end user, not the features of the product or offer.
Funnel
- After the user hits the landing page, there needs to be a cohesive flow that you want the user to accomplish.
- This goal should be easily outlined as steps that the user needs to achieve and be synonymous with the campaign goal.
- Your KPIs for your funnel should sync up with the KPIs for your campaign. Each step needs to be recorded and tracked.
Pro tip: You must always consider the customer’s journey when implementing Facebook/Meta Ads. For your user journey, you must have a cohesive funnel outlined on your Facebook/Meta campaigns. Sending users to a contact form on a self-hosted website will yield low quality, expensive results.
Therefore, “boosting” posts that don’t have a strategy behind them is not going to yield the results that you expect from your campaign. The major goal is to make sure there is some level of cohesiveness throughout your campaign from ad to conversion.
Pixel/cAPI
- The pixel should be installed on the landing page and any relevant pages that will be used in Facebook/Meta Ad efforts. The pixel can be installed sitewide with a generic “PageView” event. This differs from the View Content event.
- Your pixel should fire on each funnel event.
- Your pixel can be a source of custom audiences.
Ad Account
- Ad accounts are found within https://business.Facebook.com.
- Refrain from running ads on a personal account.
- Each new business should have its own business ad account and pixel.
- The same campaign can perform differently across each ad account due to various factors including pixel data, site data, and level of optimization.
Audience
Each audience target is considered its own ad set.
- The same ad can run on multiple ad sets or audience targets.
- Audiences can be custom audiences, lookalike audiences, interest-based, demographic-based, or location-based.
- Audience sizes will vary depending on how you set them up.
- There is no ideal audience size. Sometimes large audiences are suitable for the campaign goal, sometimes small.
- Segment each ad set into its own separate audience targeting.
- You can exclude non-performing or overlapping audiences for optimal performance.
Placement
Each placement is unique to Facebook/Meta’s assets.
- There are many to choose from and this should coincide with your particular campaign goal. Each placement has a different condition and performance parameter.
- The most popular placements are feeds, specifically Facebook/Meta News Feed.
Here are all the current, at the time of publishing, available placements on Facebook:
Feeds
- Facebook Feed
- Instagram feed
- Facebook Marketplace
- Facebook video feeds
- Facebook right column
- Instagram Explore
- Instagram Explore home
- Instagram Shop
- Messenger inbox
- Facebook Business Explore
Stories and Reels
- Instagram Stories
- Facebook Stories
- Messenger Stories
- Instagram Reels
- Facebook Reels
In-stream
- Facebook in-stream videos
Overlay and post-loop ads on Reels
- Facebook Reels
Search
- Facebook search results
Messages
- Messenger sponsored messages
In-article
- Facebook Instant Articles
Apps and sites
- Audience Network native, banner and interstitial
- Audience Network rewarded videos
- Audience Network in-stream videos
How to measure Facebook/Meta Ad success
Your individual campaign goals will determine the most relevant KPIs and how to arrange your Facebook columns. Most campaigns, however, will have certain benchmark KPIs:
General metrics
- Amount spent – The total amount spent in the account’s currency.
- Budget – The total type and frequency of budget set on the campaign level. This can be either lifetime or daily budgets.
- Delivery – The status of the campaign or ad set.
Top of funnel (ToFu)
- Creative – The actual advertisement in your ad set. This can be an image, video, or messenger ad.
- Impressions – The number of views that your ad has had.
- CTR (all) – Click through rate (all) refers to the rate of engagement. A good goal for this is 10%
- CTR (link) – Click through rate (link) is the number of clicks divided by the number of impressions. This metric measures the relevance of your ad’s call to action. A good goal for this is 1%
- Video average watch time – The average time that Facebook/Meta users watched your video creative. A good goal is 8-11 seconds.
- Cost per mille (CPM) – Your cost per 1000 impressions. The lower the better, though it’s not completely correlated to performance due to algorithmic interference.
- Cost per click (CPC) – Your cost per individual ad click. The lower the better, though it’s not completely correlated to performance due to algorithmic interference.
- Post comments – The number of comments on your post.
- New messaging connections – The number of users creating new Facebook/Meta Messenger connections with you.
- Cost per new messaging – Your cost per interaction via Facebook/Meta Messenger.
- Link clicks – The number of link clicks you have on your ad.
- Frequency – The ratio of users to impressions your ad has had. A higher number in frequency indicates that out of the impressions, users see the ad more than once.
Middle of funnel (MoFu)
- Landing page – The page that users land on after they click on an ad.
- View content (VC) – The first page event that is recorded by the Facebook/Meta Pixel. This indicates if the user has interacted with the page long enough to load the pixel and fire the event.
- Cost per view content (VC) – The amount spent divided by the number of content views. The lower the better.
- Add to cart (ATC) – The number of users who add a product to the cart (eCommerce only). The higher the better.
- Cost per add to cart – Your amount spent over the number of add to carts. The lower the better.
- Initiate checkout (IC) – The event that the pixel fires when the user has loaded the checkout page (eCommerce only). The higher the better.
- Cost per initiate checkout – Amount spent divided by the number of initiate checkout events. The lower the better
Bottom of funnel (BoFu)
- Offer – What the user stands to gain from clicking on the ad, i.e.the reason why you want your customers to visit your landing page.
- Website purchases – The number of purchases you’ve had on your website from your Facebook/Meta ads.
- Leads – A potential opportunity obtained from the final conversion step.
- Cost per lead – The amount spent divided by number of leads.
- Results – The number of completions that you’re obtaining from your set campaign goal.
Pro tips: Inventory, quality ranking, and engagement all impact the price or the CPM of your ads. This can be changed and is contingent on how engaging your ad is to the selected audience. Engagement is another way to measure the response to the ad in the marketplace. A positive response means that the ad will perform well, have a high CTR all, lower CPC, high CTR link and low CPM compared to other ads in the marketplace.
This is very important. You don’t need to be the best, you need to be better than your competition. Since Facebook/Meta ads is a marketplace where ads compete against each other, Facebook/Meta determines your quality compared to other users on the platform. It’s a self-optimizing mechanism. For most startups and businesses, the goal of website conversions will be the best option. This can be useful to determine which placements to keep and which to optimize off. In most cases, when starting out, you select the “all placements” option.
The recipe for a successful campaign
- Set Goals. Identify your individual campaign goals and what you want out of Facebook/Meta Ads.
- Target the most relevant audiences for your offer. Not all audiences will work.
- Split test everything. Yes, you need to test many audiences, creative versions, offers, and landing page combinations to find the winning strategy.
- Keep testing new creative, even if the existing creative is performing satisfactorily.
- Try new angles. If a direct offer isn’t working, try an informational piece before the landing page. If leads are not high quality, find ways to filter them out. Keep trying new angles with your offer until one resonates with your audience
- Ongoing maintenance. Keep track of your campaigns and make sure there is no significant change in the KPIs you are tracking.
- Refresh poor performing campaigns. If you have a campaign that was performing well in the past, try duplicating the entire campaign and refreshing it.
- Have a great landing page and offer. These two components are crucial for campaign success. Not all offers, placements and audiences will perform all the time.
- Measure your results within your conversion window (1 or 7 days). Don’t panic if you’re not getting immediate results. Optimization will take time.
- Relax. You will spend money, but if you maintain a cool, non-emotional approach to your advertising, you will be able to see the metrics clearly.
- Measure your success. Compare week-on-week spreads of the campaign and notice if the campaign KPIs are holding steady, decreasing or increasing. This will tell you if your ad is relevant in the marketplace. For example, a high CPM and a low CTR (all) indicate that your audience is not really engaging with your post compared to other users in the marketplace. Therefore, Facebook/Meta will charge you more for the same traffic.
How to launch Facebook/Meta Ads for the first time
General
- Conduct competitive analysis. Find out what your competitors are doing. Focus on the highest engagement posts and pages to gain an idea of what works and what doesn’t.
- Spend some money. The goal is to recoup your spend through ROI-focused campaigns.
- Define your goals. Each campaign will have different goals. Define your goals for your campaign and plan it out before spending resources.
Lead Generation
- Perform competitive research. Identify what copy, images, landing pages and funnels your competition is using.
- Determine what a lead means for your business. A lead can mean many things to many businesses. What does the lead look like to your business? Determine what your offer will be. How are you going to serve your market? What product or service are you intending on offering to your customers?
- Determine the benefits of the offer for the lead. If your product or service is consumed by your target market, what benefits are expected from using your product or service?
- Build your landing page and funnel around the benefits of your offer for your lead. The landing should focus on benefits first, then features.
- Select three of the most obvious audience types for your offer. Split test three or more audiences to determine the precise target audience for your offer. For local campaigns, focus on the local area that you want to target.
- Each audience should be about 1-2M in size.
- Leave placements open until you know which placements work for your campaign. You can use the break-out feature to learn more once your campaign has sufficient impressions.
- Optimize for either the view content or lead events on your Facebook/Meta Pixel. On the ad set level, you will be able to select the event you want to optimize for in your campaign.Test lead campaign and conversion campaign to determine quality and performance difference. Facebook/Meta can generate leads with native forms. See if native forms perform better for you than an external page or form.
eCommerce
- Perform competitive research. Identify what copy, images, landing pages and funnels your competition is using.
- Determine the goal of the campaign. Are you looking for brand exposure or are you looking for conversions?
- Select a meaningful conversion. If you’re looking for conversions, select a conversion campaign and target view content, add to cart, initiate checkout, or purchase events for your conversion campaign. To help you decide, select an event that occurs at least 50 times within the conversion or attribution window (1 or 7 days). The higher the frequency of occurrence of the event, the more data the machine-learning algorithm has to optimize.
- Split test the same audience (usually the one that is most obvious) with different creatives using a dynamic ad, on the ad set level, to determine a good ad image/video/text combination.
- Implement look-a-like audiences. If you have an existing customer list or opt-in list, you can upload this into Facebook/Meta and create a custom audience. From there, you can use this audience to create a look-a-like audience that can be used for targeting on the ad set level.
- Test audiences. Test your product with several interest-based audiences, lookalike audiences, and behavior targeting.
- Monitor your overall KPIs and most importantly your ROAS to determine in which direction to take the campaign. If results are positive ROI, adding more budget to a CBO campaign would allow you to reach more of the audience that’s converting.
- Learn how to run Shopify Facebook Ads when you have multiple products to test in your store.
Retargeting
- Retarget organic and paid traffic from any source as long as the user loaded the Facebook/Meta pixel.
- Determine a logical offer based on the user’s position within your funnel. The offer that is presented on retargeting campaigns need to be logical derivatives of the initial advertisement or landing page.
- Create a custom audience. Build audiences that you want to use for retargeting campaigns. Audiences can be based on events and existing pixel data from any traffic source. The pixel stores a rolling 180 days of data on each event.
- Use the custom audience as an audience on the ad set, instead of any interests, behaviors or lookalikes.
- Build a creative that is suitable for the audience within their existing stage of the funnel.
- Split test creative and landing pages the way your organization normally would.
- Measure the performance and determine the optimal experience post-initial ad exposure.
Various Facebook/Meta Ad strategies
50% video view
Run a video view campaign against multiple audiences at the ad set level with a video ad. In parallel, create a retargeting campaign using a custom audience of those who watched 50% of the video. Once a sufficient amount of people have watched 50% of the video (minimum 200), build a look-a-like audience using the custom audience and repeat the process. Use the winning creative(s) determined during the initial testing phase throughout the scaling phase.
Content marketing
Run a piece of content on a conversion campaign against multiple audiences at the ad set level with multiple creatives. Accumulate view content audience. Remarket the offer to the view content audience. Once you have about 200 view content fires (the more the better), build a look-a-like audience off the custom audience and repeat the process. Use the winning creative(s) determined during the initial testing phase throughout the scaling phase.
Direct sales
Run the offer directly on a conversion campaign (ATC, IC, or purchase) against multiple audiences at the ad set level with multiple creatives. Test many different campaign styles. Build custom audiences based on purchasers and build look-a-likes based on purchasers for additional direct sales. Add budget to your CBO at 25%/day until you stabilize revenue.
Facebook/Meta Ad tools
Here are some Facebook/Meta Ad tools to help you research your competition, build your creative, test your landing pages, and build your campaigns and ad sets.
There are dozens of other tools, but these are a good starting point. Use your own goals and determine your best use case for the tools.

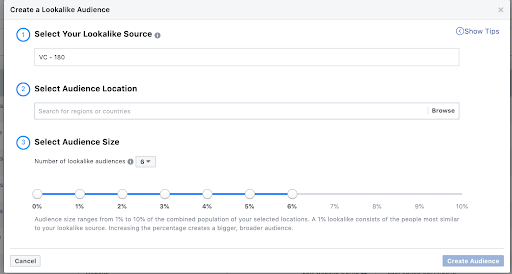
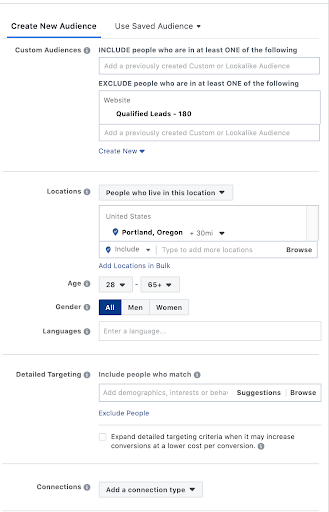 Each audience target is considered its own ad set.
Each audience target is considered its own ad set.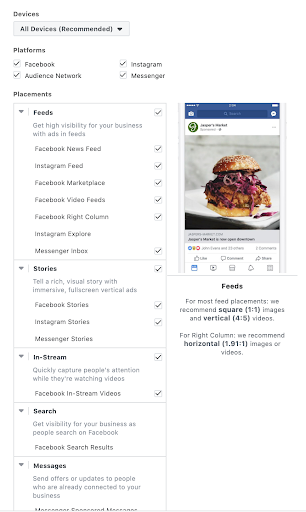 Each placement is unique to Facebook/Meta’s assets.
Each placement is unique to Facebook/Meta’s assets.